What is a solar inverter?
An inverter plays a vital role in power electronics by actively converting DC power into usable AC electricity. Common DC sources such as batteries and solar panels feed power into the system, while traditional AC electricity comes from power plants through complex transmission networks to supply homes and industries. Inside every inverter, you’ll find three key elements working together: an inverter bridge, control logic, and filter circuits that ensure smooth operation.
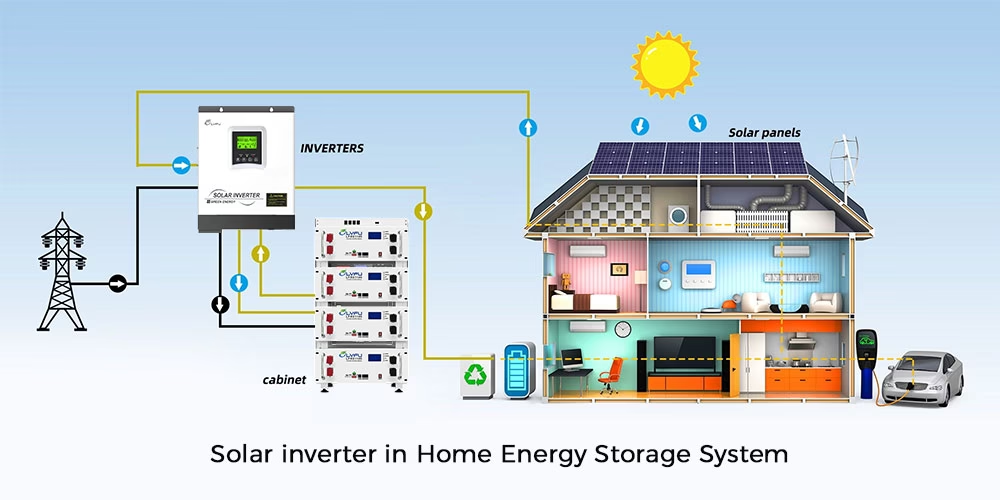
Importance of solar inverter
Acting as the heart of a solar photovoltaic power generation system, the photovoltaic inverter performs several critical functions. During normal operation, it converts the DC power generated by photovoltaic modules into AC power. This AC electricity then powers local loads, feeds into the grid, or alternatively, the system can store DC power directly in batteries.
A particularly crucial function occurs during power outages: the inverter immediately begins drawing DC power from the batteries and converts it into usable AC power for the user’s appliances. Beyond this emergency role, the inverter enables flexible two-way conversion between grid power and battery storage. This vital capability fundamentally overcomes the traditional limitation where photovoltaic systems could only operate during daylight hours, solidifying the inverter’s indispensable role in the entire energy system.
Classification of solar inverter
Grid-tie Inverter
A grid-tie inverter represents a specialized category of power conversion equipment. Its core operational principle enables direct synchronization between the converted AC output and the mains grid, allowing excess power to feed back into the grid without requiring battery storage. For enhanced performance, modern designs frequently incorporate MPPT technology within their input circuits to optimize energy harvesting efficiency.
Off-grid inverter
Off-grid inverters typically connect directly to solar panels, small wind turbines, or other DC power sources, where they perform the crucial task of converting DC electricity into standard AC power for household use. These systems primarily draw energy from integrated battery banks to operate electrical appliances. True to their name, off-grid inverters function in complete isolation from public utility grids, establishing fully independent power systems that require no external electrical supply.
Hybrid inverter
Generally, the term hybrid inverter can have two different meanings. One common version is an off-grid inverter with a built-in solar charge controller, while the other is a more versatile, integrated off-grid inverter that can be used in grid-connected photovoltaic systems. A significant advantage is that its battery storage can be flexibly configured according to needs.

