An off-grid solar power system provides a self-sufficient electricity supply. It operates independently of the traditional power grid. This setup primarily relies on solar energy, which is a clean and renewable resource. In some cases, the system can also integrate other renewable sources like wind power. For added stability and reliability, a diesel generator may supplement the overall supply.
photovoltaic (PV) power system
Consider a typical photovoltaic (PV) power system as an example. Its core components include a solar array, an energy storage battery bank, and a central control unit. Overall, such a system is both environmentally friendly and highly practical. It reliably delivers stable power to remote areas or regions where extending the grid is difficult.
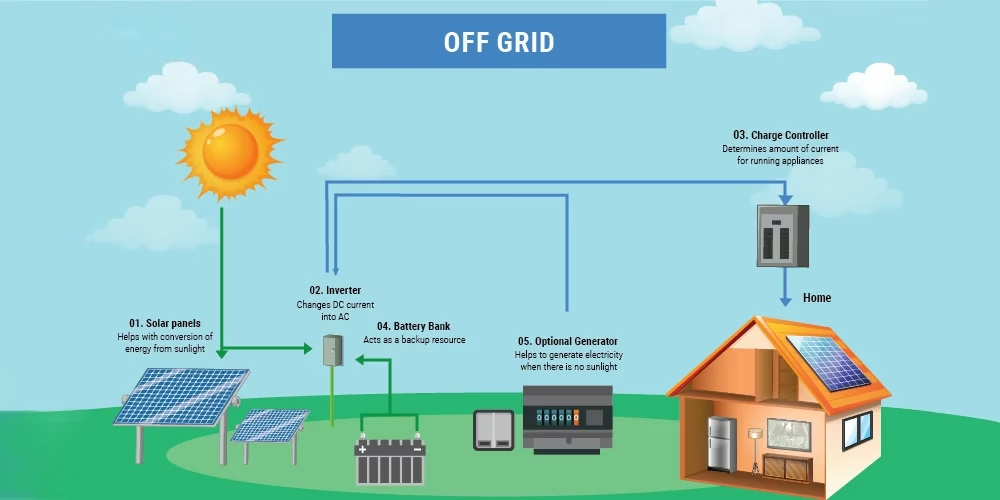
Diagram of a Hybrid System
Energy Storage Batteries
Energy storage batteries play a crucial role in the entire energy system. They not only guarantee the power supply when renewable sources like solar or wind are intermittent or unavailable but also ensure the continuity and stability of the system’s power output. Although storage batteries are one of the most expensive components in the system, their long-term value and function are evident. By storing renewable energy, these batteries can reliably power the load during unfavorable weather conditions, thereby optimizing energy utilization efficiency.
Lead-Acid Gel Batteries and Lithium-Ion Batteries
The most commonly used batteries today can be broadly divided into two categories: Lead-Acid Gel Batteries and Lithium-Ion Batteries. Next, we will discuss the differences between these two types.
Lead-acid gel batteries offer high cost-effectiveness and a simple structure. Because of this, they are widely used in cost-sensitive projects. They also perform well in low-temperature environments where safety is a major concern.
Another advantage is their straightforward maintenance. Unlike many modern batteries, they don’t require a complex Battery Management System (BMS) for monitoring.
However, these batteries do come with some drawbacks. Their service life is relatively short, typically lasting just 3 to 5 years. Their deep cycle capability is also limited, usually ranging from 400 to 700 cycles.
Furthermore, lead-acid batteries have a low energy density of about 30-40 Wh/kg. This means they are bulkier and heavier for the same amount of stored energy. In terms of performance, their conventional discharge rate is 0.2C. Consequently, they aren’t suitable for applications that need rapid power bursts.
Despite these limitations, lead-acid gel batteries remain a reliable and economical choice for many specific scenarios.

Illustration of a PV Energy Storage Gel Battery
Lithium-ion batteries are crucial for modern energy storage. This is particularly true for Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and ternary lithium types, thanks to their standout performance.
Take LiFePO4 batteries as an example. They deliver an impressive deep cycle life of over 4,000 cycles. On top of that, their service life often exceeds 10 years. These batteries also allow a high Depth of Discharge (DOD), up to 90%, which ensures very efficient use of their stored energy.
In terms of size and weight, they offer a clear advantage. Their energy density typically falls between 150-250 Wh/kg. This means they pack more power into a smaller, lighter package. Consequently, they are an ideal choice for applications that need both portability and high energy density.
Moreover, most energy storage lithium batteries support a 1C discharge rate. This capability lets them handle high-load demands effectively. Finally, better quality models come with built-in communication features. These allow for convenient remote monitoring and management, adding a layer of smart control.

Lithium-Ion Batteries
Battery Management System (BMS)
However, the cost of lithium-ion batteries remains relatively high. This is especially true when we compare them to lead-acid gel batteries. Additionally, they require a dedicated Battery Management System (BMS). This system continuously monitors battery status to ensure both optimal performance and maximum safety.
Low-temperature use presents another challenge. In such environments, lithium batteries risk lithium-ion crystallization during charging. This crystallization can puncture the internal separator and potentially cause a short circuit. For this reason, extra heating measures are often necessary in cold climates. These steps are crucial to maintain both safety and efficiency.
Despite these factors, lithium-ion batteries are still the preferred choice for many high-end applications. Their long lifespan, high energy density, and strong discharge capability make them a compelling solution.
| Feature | Lead-AcidGelBattery | Lithium-Ion(LiFePO4)Battery |
| Initial Cost | Low | High |
| Service Life | 3-5 years | > 10 years |
| Deep Cycle Life | 400-700 cycles | > 4,000 cycles |
| Depth of Discharge (DOD) | Limited (e.g., 50%) | Up to 90% |
| Energy Density | Low (30-40 Wh/kg) | High (150-250 Wh/kg) |
| Discharge Rate | Low (0.2C) | High (1C) |
| BMS Requirement | Not required | Required |
| Low-Temp Performance | Good (Simple structure) ) | Requires heating for charging |
| Maintenance | Simple | Remote monitoring/management possible |
When choosing between lithium and lead-acid batteries, you need to weigh several key factors. Consider cost, performance, maintenance, safety, and environmental impact.
Now, lithium batteries do come with a higher upfront price. However, they deliver a much longer service life and higher energy density. They also charge and discharge more efficiently. Plus, they operate well across a wider temperature range. All these benefits make lithium batteries ideal for high-performance, low-maintenance applications. Another major advantage is their superior intelligence, thanks to integrated management systems.
In contrast, lead-acid batteries require a lower initial investment. The trade-off is lower energy density, more frequent maintenance, and a shorter overall lifespan. These batteries fit well where budgets are tight. They also work for situations that don’t demand top-tier performance, like some basic backup power systems.
So, what’s the final take? If your project needs high performance, long life, and a smaller environmental footprint, lithium batteries are usually the better option. But if you’re on a strict budget and the performance demands are modest, lead-acid batteries can be a practical, cost-effective solution. Remember, the smart choice involves looking beyond the purchase price. Always consider the long-term Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) and how the battery will perform over its entire expected lifespan.

